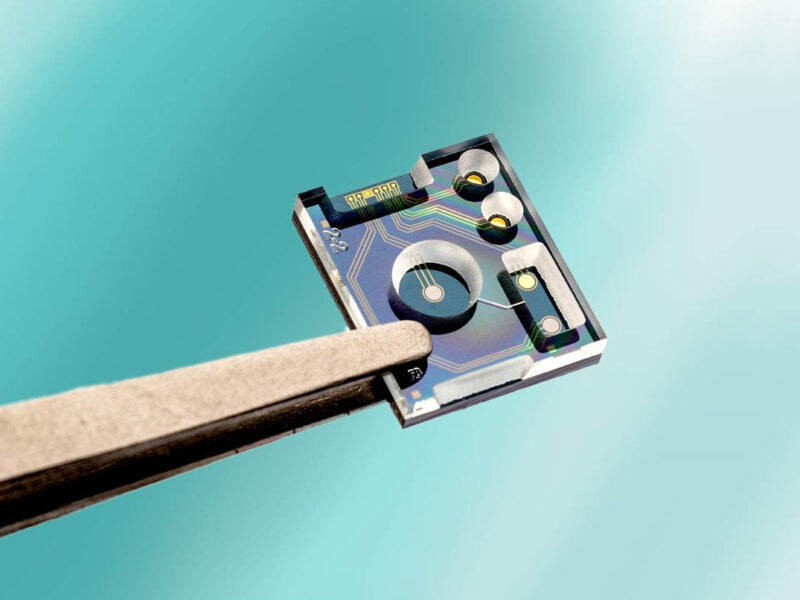
Miniature multi-ion IoT sensor tests pH, chloride levels in fluid
With the possibilities of SoC (system on chip) integration it may enable massive and cost-effective deployments in Internet-of-Things (IoT) settings. Its innovative electrode design results in a similar or better performance compared to today’s standard equipment for measuring single ion concentrations and allows for additional ion tests.
Sensors based on ion-selective membranes, imec says, are considered the “gold standard” to measure ion concentrations in many applications, such as water quality, agriculture, and analytical chemistry. They consist of two electrodes, the ion-sensitive electrode with the membrane (ISE) and a reference electrode (RE).
When these electrodes are immersed in a fluid, a potential is generated that scales with the logarithm of the ion activity in the fluid, forming a measure for the concentration. However, the precision of the sensor depends on the long-term stability of the miniaturized RE, a challenge that imec says has now been overcome.
“The common issue with such designs is the leaching of ions from the internal electrolyte, causing the sensor to drift over time,” says Marcel Zevenbergen, senior researcher at imec/Holst Centre. “To suppress such leaching, we designed and fabricated an RE with a microfluidic channel as junction and combined it with solid-state iridium oxide (IrOx) and silver chloride (AgCl) electrodes fabricated on a silicon substrate, respectively as indicating electrodes for pH and Cl-. Our tests demonstrated this to be a long-term stable solution with the sensor showing a sensitivity, accuracy and response time that are equal or better than existing solutions, while at the same time being much smaller and potentially less expensive.”
“We are providing groundbreaking sensing and analytics solutions for the IoT,” says John Baekelmans, Managing Director of imec in The Netherlands. “This new multi-ion sensor is one in a series that Holst Centre is currently developing with its partners to form the senses of the IoT. For each sensor, the aim is to leapfrog the current performance of the state-of-the-art sensors in a mass-producible, wireless, energy optimized and miniaturized package.”
imec: www.imec.be
Holst Centre: www.holstcentre.com
Related articles:
Implanted biosensor chip can monitor blood chemistry, drugs
Wearable sensor analyzes sweat to monitor health
Disposable sensor detects wound infections in seconds
AMS: Building on the ‘four pillars of sensing’
 If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News
If you enjoyed this article, you will like the following ones: don't miss them by subscribing to :
eeNews on Google News




